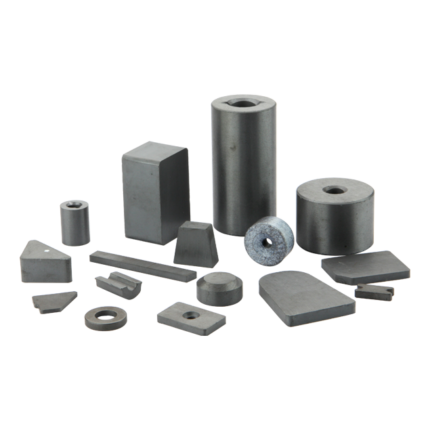
Bonded Pressed NdFeB Magnets: Overview
Bonded NdFeB magnets, composed of Nd₂Fe₁₄B, are synthetic magnets manufactured by mixing rapidly quenched NdFeB magnetic powder with a binder. These magnets are shaped using compression molding or injection molding techniques. They feature high dimensional precision and the ability to form complex magnetic components with multi-pole orientation in a single process. Bonded NdFeB magnets exhibit excellent mechanical strength, allowing simultaneous integration with other components during forming.
Background
The concept of bonded magnets emerged in the 1970s, when SmCo magnets were already commercialized. While sintered permanent magnets had significant market appeal, they faced challenges such as difficulty in machining into complex shapes, susceptibility to cracking or chipping, and assembly issues. These limitations led to the development of bonded magnets by crushing permanent magnet materials, mixing them with plastic binders, and pressing them in magnetic fields.
With the introduction of NdFeB permanent magnet powders offering superior magnetic performance, flexible bonded magnets rapidly gained popularity. Bonded NdFeB magnets have seen widespread adoption due to their:
- Low cost.
- High dimensional accuracy.
- Design flexibility.
- Superior mechanical strength.
- Lightweight nature.
The annual growth rate for bonded NdFeB magnets is approximately 35%.
Advantages of Bonded Pressed NdFeB Magnets
- Mechanical Strength: Exceptional mechanical robustness with smooth surface finish.
- Tight Tolerances: Compression-molded NdFeB can achieve highly precise tolerances.
- Impact Resistance: Superior resistance to chipping compared to other rare-earth magnets.
- High Energy-to-Weight Ratio: Efficient performance in compact designs.
- Flexible Shapes and Sizes: Can be molded into various complex geometries.
- Magnetic Performance: Maximum energy product reaches up to 10 MGOe.
- Single-Step Manufacturing: Capable of multi-pole magnetization in one step.
- Low Mold Costs: Economical tooling requirements.
- Corrosion Resistance: Effective surface treatments prevent oxidation and degradation.
- Wide Applications: Used in micro-motors, automotive motors, air conditioning motors, automation devices, sensors, actuators, telecommunication, instrumentation, and more.
- Temperature Stability: Operates stably at temperatures up to 150°C.
Applications
Since its development in 1988, bonded NdFeB has seen rapid growth and is widely utilized in applications where compact, lightweight, and high-performance magnets are essential. Key application areas include:
- Office Automation: Printers, copiers, and scanners.
- Electric Drives: Miniature motors and automated equipment.
- Consumer Electronics: Mobile phones, CD-ROM/DVD-ROM drives, hard disk drive spindles, and other micro DC motors.
- Automotive Applications: Electric motors for vehicles.
- Sensors and Actuators: Precision components in instrumentation and telecommunication industries.
Comparison with Sintered NdFeB Magnets
- Manufacturing Simplicity: Bonded NdFeB requires no secondary machining and enables the formation of intricate shapes, reducing motor size and weight.
- Dimensional Precision: Enables tighter tolerances compared to sintered magnets.
- Single-Step Integration: Bonded magnets can incorporate other components during molding.
Performance and Grades of Bonded Pressed NdFeB Magnets
| Grade | Remanence | Coercivity | Intrinsic Coercivity | Maximum Magnetic Energy Product | Average Reversible Temperature Coefficient | Max Temp | Curie Temperature | ||||
| mT | kGs | kA/m | kOe | kA/m | kOe | kJ/m³ | MGOe | %/ ℃ | ℃ | ℃ | |
| BN-2 | 300-400 | 3.0-4.0 | 160-240 | 2.0-3.0 | 480-640 | 6.0-8.0 | 16-24 | 2.0-3.0 | -0.11 | 120 | 120 |
| BN-4 | 400-500 | 4.0-5.0 | 240-320 | 3.0-4.0 | 560-720 | 7.0-9.0 | 32-44 | 4.0-5.5 | -0.11 | 120 | 120 |
| BN-6 | 500-600 | 5.0-6.0 | 320-400 | 4.0-5.0 | 560-720 | 7.0-9.0 | 48-60 | 6.0-7.5 | -0.11 | 120 | 120 |
| BN-8 | 600-680 | 6.0-6.8 | 360-440 | 4.5-5.5 | 640-800 | 8.0-10 | 60-72 | 7.5-9.0 | -0.11 | 150 | 150 |
| BN-8H | 600-650 | 6.0-6.5 | 400-480 | 5.0-6.0 | 1040-1360 | 14.0-16.0 | 60-68 | 7.5-8.5 | -0.12 | 160 | 160 |
| BN-8L | 650-680 | 6.5-6.8 | 400-480 | 5.0-6.0 | 900-1120 | 11.0-13.0 | 64-72 | 8.0-9.0 | -0.13 | 160 | 160 |
| BN-9 | 600-680 | 6.0-6.8 | 400-480 | 5.0-6.0 | 640-800 | 8.0-10.0 | 68-72 | 8.5-9.5 | -0.11 | 150 | 150 |
| BN-10 | 680-730 | 6.8-7.3 | 400-480 | 5.0-6.0 | 640-800 | 8.0-10.0 | 76-84 | 9.5-10.5 | -0.10 | 150 | 150 |
| BN-12 | 710-750 | 7.1-7.5 | 440-520 | 5.5-6.5 | 720-880 | 9.0-10.0 | 84-96 | 10.5-12.0 | -0.10 | 150 | 150 |
| BN-12L | 720-760 | 7.2-7.6 | 400-480 | 5.0-6.0 | 480-640 | 6.0-8.0 | 84-96 | 10.5-12.0 | -0.11 | 140 | 140 |
Physical Properties of Bonded NdFeB Magnets
| Parameter name | Bonded NdFeB Magnets |
| Curie Temperature(℃) | 325 |
| Max Working Temp(℃) | 150 |
| Hardness Hv(MPa) | 80-120 |
| Density(g/cm3) | 5.8-6.2 |
| Resistivity(Ω·cm) | 0.026 |
| Compressive Strength(%/℃) | -0.17 |
| Flexural Strength(kg/mm) | 25 |
| Temperature Coefficient(kgf/mm2) | 3 |
Bonded NdFeB magnets excel in high-performance, precision applications, offering unparalleled flexibility, cost-efficiency, and magnetic strength. Their adaptability to complex shapes and reliable thermal stability ensures they remain a critical component across diverse industries.